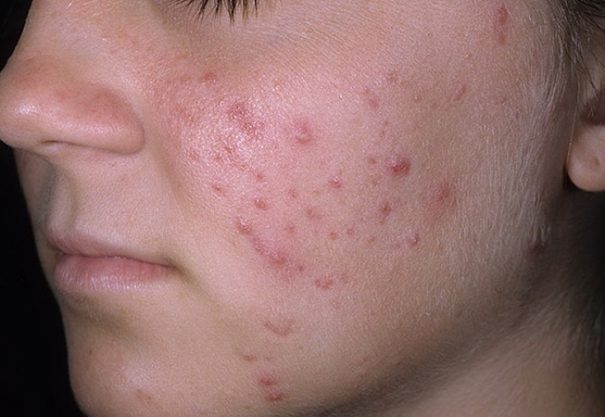
Pink acne
Overview of Rosacea
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that causes redness of the skin and a rash, usually on the nose and cheeks. It can also cause eye problems. Symptoms usually come and go, and many people report that certain factors, such as sun exposure or emotional stress, trigger them.
There is no cure for rosacea, but treatment can keep it under control. The choice of treatment will depend on the symptoms and usually involves a combination of self-help measures and medications.
Who gets rosacea?
Anyone can get rosacea, but it is most common among the following groups:
- Middle and older adults.
- Women, but when men get it, it tends to be more severe.
- Fair-skinned people, but in darker-skinned people, it may be underdiagnosed because dark skin can mask facial redness.
People with a family history of rosacea may be at increased risk for the disease, but more research is needed to understand the role genetics play.
Rosacea symptoms
Most people experience only some of the symptoms of rosacea, and the nature of the symptoms varies from person to person. Although it is a chronic (long-term) condition, rosacea often alternates between flare-ups and periods of remission (no symptoms).
Rosacea symptoms include:
- Redness of the face. It may start out as a tendency to blush or blush, but over time, the redness may persist for a longer time. This is sometimes accompanied by a tingling or burning sensation, and reddened skin can become rough and flaky.
- Rash. Reddened areas of the face may develop red or pus-filled bumps and pimple-like pimples.
- Visible blood vessels. They usually appear as thin red lines on the cheeks and nose.
- Skin thickening. The skin may thicken, especially on the nose, giving the nose an enlarged and bulging appearance. This is one of the more serious symptoms and it mostly affects men.
- Eye irritation. In what is known as ocular rosacea, the eyes become inflamed, red, itchy, watery, or dry. They may appear gritty or as if they have something in them, such as an eyelash. The eyelids may swell and become red at the base of the eyelashes. Barley may develop. It is important to see a doctor if you have eye symptoms because if left untreated, it can lead to eye damage and loss of vision.
Sometimes rosacea progresses from temporary redness of the nose and cheeks to more permanent redness and then to a rash and small blood vessels under the skin. If left untreated, the skin can thicken and enlarge, resulting in firm red bumps, especially on the nose.
The disease usually affects the central part of the face, but in rare cases it can spread to other parts of the body, such as the sides of the face, ears, neck, scalp, and chest.
Causes of Rosacea
Scientists don't know what causes rosacea, but there are a number of theories. They know that inflammation contributes to some key symptoms, such as skin redness and rashes, but they don't fully understand why inflammation occurs. In part, this may be due to the increased sensitivity of the skin in people with rosacea to environmental stressors such as ultraviolet (UV) radiation and microorganisms that inhabit the skin. Both genetic and environmental (non-genetic) factors likely play a role in the development of rosacea.
Leave a Reply