Stages of the menstrual cycle
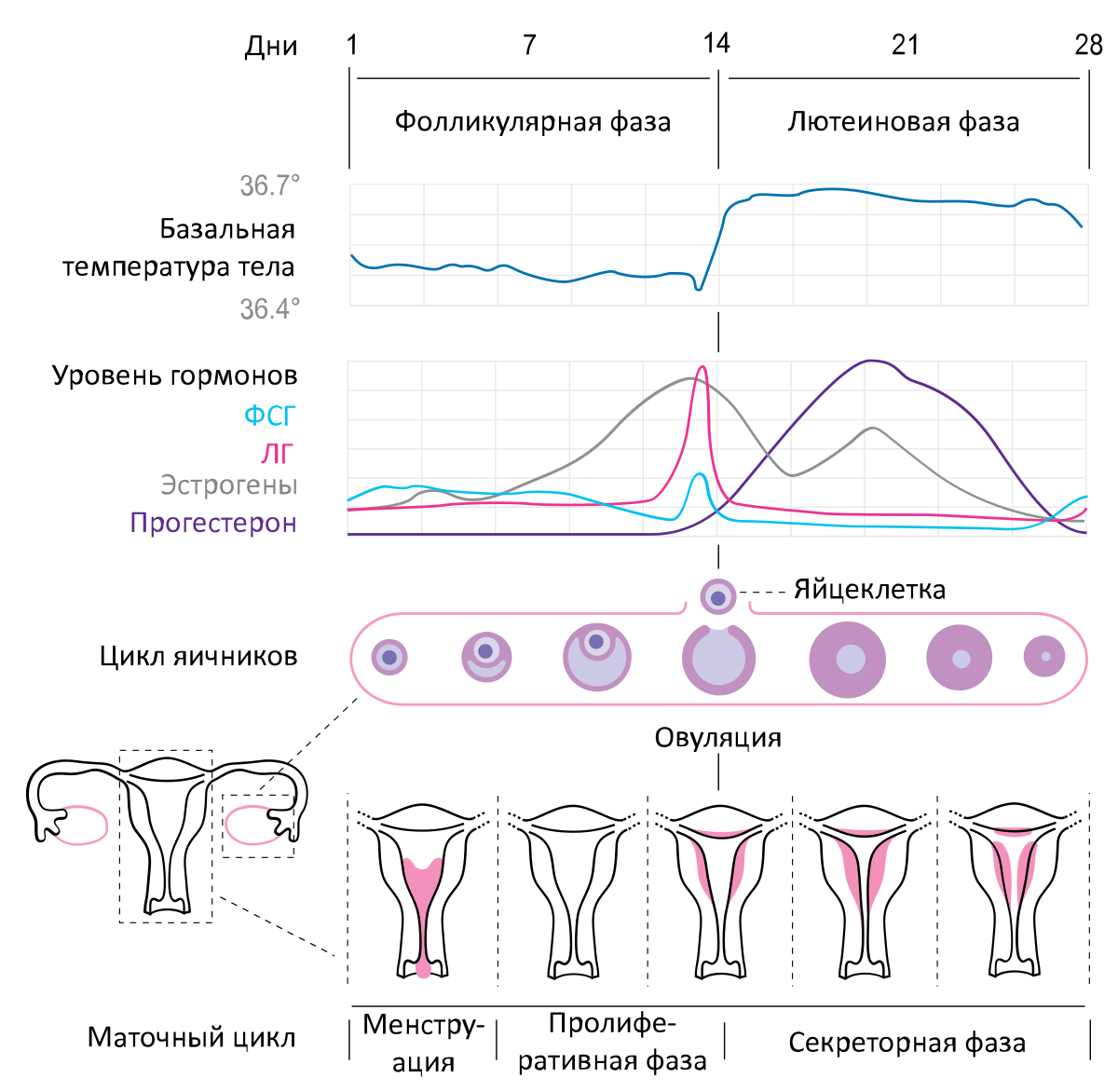
The menstrual cycle is a period of time that repeats on average every 28 days. Thus, the woman's body prepares for fertilization. The menstrual cycle consists of three processes: the endocrine cycle, the ovulatory (ovarian) and endometrial (uterine) cycle. The hypothalamus and pituitary gland send signals to the ovaries and uterus. All activities are interdependent.
Watch the video: "Sexy Personality"
1. What are the stages of the menstrual cycle?
- Hormonal cycle
Ovarian function depends on two hormones: luteinizing hormone and follitropin. These hormones are secreted by the pituitary gland. But in order for the pituitary gland to produce lutein and follitropin, it must be treated with GnRH (a hormone secreted by the hypothalamus).
Menstruation causes an increase in the level of follicle-stimulating hormone. Thus, the ovaries are stimulated to form and develop the Graaff follicle. There may be several bubbles. This is where the egg matures. Estrogens are secreted by the walls of the released follicles.
Estrogens are hormones that determine certain sexual characteristics of a woman (uterus, fallopian tubes, external genitalia) and her ability to achieve orgasm. The level of follitropin rises. Due to this, one of the bubbles begins to dominate the others. This follicle secretes more and more estrogen, which lowers follitropin levels. This is where feedback comes into play. Follitropin is responsible for the initial development of follicles. In turn, lutotropin for the phase of their decline, i.e. ovulation.
Thanks to follitropin, an egg is released from the Graaff follicle. The remnants of the follicle under the action of the hormone turn into a corpus luteum, which produces estrogen and progesterone. When fertilization does not occur, the corpus luteum dies. Estrogen and progesterone are no longer produced. The pituitary gland prepares for the next cycle. So he again begins to produce follitropin.
- ovarian cycle
Each girl after birth has a certain number of eggs, which is her reserve for life. The eggs are surrounded by primordial follicles. There are about 400 such follicles in the ovaries. Each follicle contains one egg. The pituitary gland begins to produce follitropin. This is the stimulus for the follicles to start developing. The bubbles swell when filled with liquid, forming a bubble cavity.
Part of the cells inside the follicle are located in the appendage facing the lumen of the follicle. The rest of the cells move outward and form a granular layer. Only one follicle is developed enough to survive. Others are dying. The walls of the developed follicle produce estrogens that stimulate the pituitary gland. The pituitary gland produces luteinizing hormone. Thanks to this hormone, ovulation is possible, that is, the release of an egg.
When ovulation occurs and how long it takes to ovulate are key considerations when using natural methods of contraception. This requires a good understanding of one's own body. Sometimes it happens to a woman anovulatory cycle. The remnants of the follicle under the action of luteinizing hormone turn into a corpus luteum. If fertilization fails, the body turns from yellow to whitish and dies.
The menstrual cycle (menstruation) is the first cycle phase. It takes about 5 days. In the second phase, during the ovarian cycle, the follicle matures. This is day 6-14 of the cycle. This phase is called the follicular phase. The final phase (luteal phase) continues from ovulation to rebleeding. It falls on days 15-28. The first day of bleeding is also the first day of the cycle. On the other hand, the last day of the cycle is the day before rebleeding.
- uterine cycle
The lining of the uterus changes to some extent during the cycle. Under the influence of estrogens, its tissues become thicker and larger. When exposed to progesterone on the uterus, the mucosa begins to secrete a special fluid that the embryo feeds on. If fertilization is not achieved, the mucosa begins to flake off.
Enjoy medical services without queues. Make an appointment with a specialist with an e-prescription and e-certificate or an examination at abcHealth Find a doctor.
Leave a Reply